15 changed files with 843 additions and 0 deletions
+ 38
- 0
.github/ISSUE_TEMPLATE/bug_report.md
|
|||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
+ 20
- 0
.github/ISSUE_TEMPLATE/feature_request.md
|
|||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
+ 128
- 0
CODE_OF_CONDUCT.md
|
|||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
+ 1
- 0
CONTRIBUTING.md
|
|||
|
|
||
BIN
Data-enabled predictive control for quadcopters.pdf
File diff suppressed because it is too large
+ 88
- 0
examples/example_mimo_twotank.ipynb
File diff suppressed because it is too large
+ 95
- 0
examples/example_siso_pulley.ipynb
BIN
examples/images/example_mimo_twotank.png
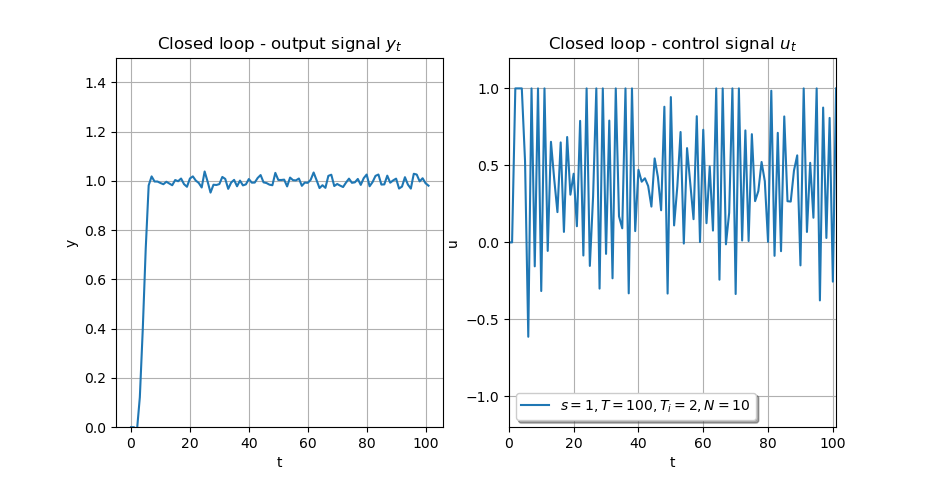
BIN
examples/images/example_siso_pulley.png
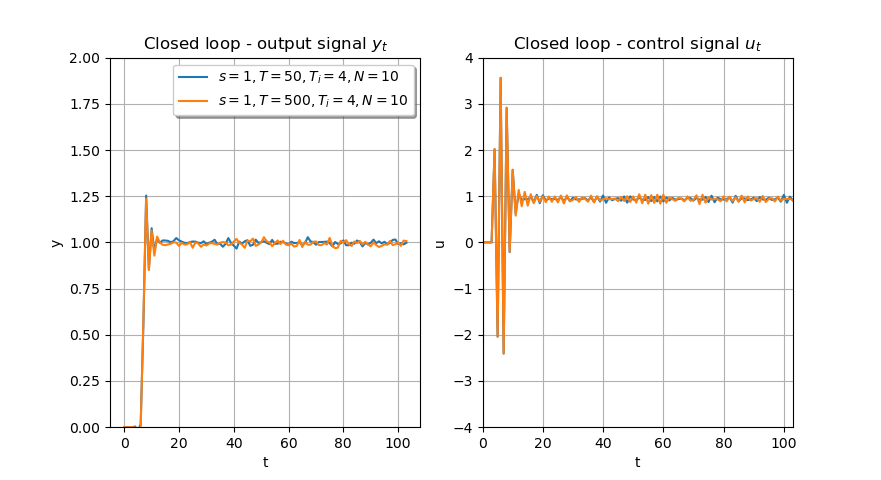
+ 70
- 0
examples/utils.py
|
|||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
+ 11
- 0
pydeepc/__init__.py
|
|||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
+ 232
- 0
pydeepc/deepc.py
|
|||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
+ 144
- 0
pydeepc/utils.py
|
|||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
BIN
requirements.txt
+ 16
- 0
setup.py
|
|||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||